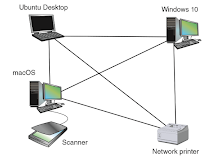
When using peer-to-peer network model, the operating system of each computer on the network is responsible for controlling access to its resources without centralized control. The computers are known as nodes or hosts on the network, form a logical group of computers and users that share resources. Each computer using peer-to-peer network controls its own administration, resources and security. Basically, it functions without any intermediary.
The types of operating system that can be installed on computers in a peer to peer network are Windows, Linux and macOS.
You can also be more open to knowing how this Peer-to-peer settings can help you in your studies as well as in the future.
Keep in mind that the connecting lines describes the logical arrangement or topology of the group of computers.
THE ADVANTAGES OF USING PEER-TO-PEER NETWORKS:
They are simple to configure. For these reason, this network type can be used where technical assistants are scarce.
They are often less expensive to set up and maintain than any other types of networks.
Built in redundancy
THE DISADVANTAGES OF USING PEER-TO-PEER NETWORKS:
They are not scalable, whereby, as a peer-to-peer network grows larger, adding or changing significant elements of the network may be difficult.
They are not necessarily secure, meaning that in simple installations, data and other resources shared by network users can be easily discovered and used by unauthorized people.
They are not practical for connecting more than a few computers because it’s too time consuming to manage the resources on the network.
Not very secure
No central point of storage or file archiving
Additional load on computer due to resource sharing
Hard to maintain version control


Comments
Post a Comment